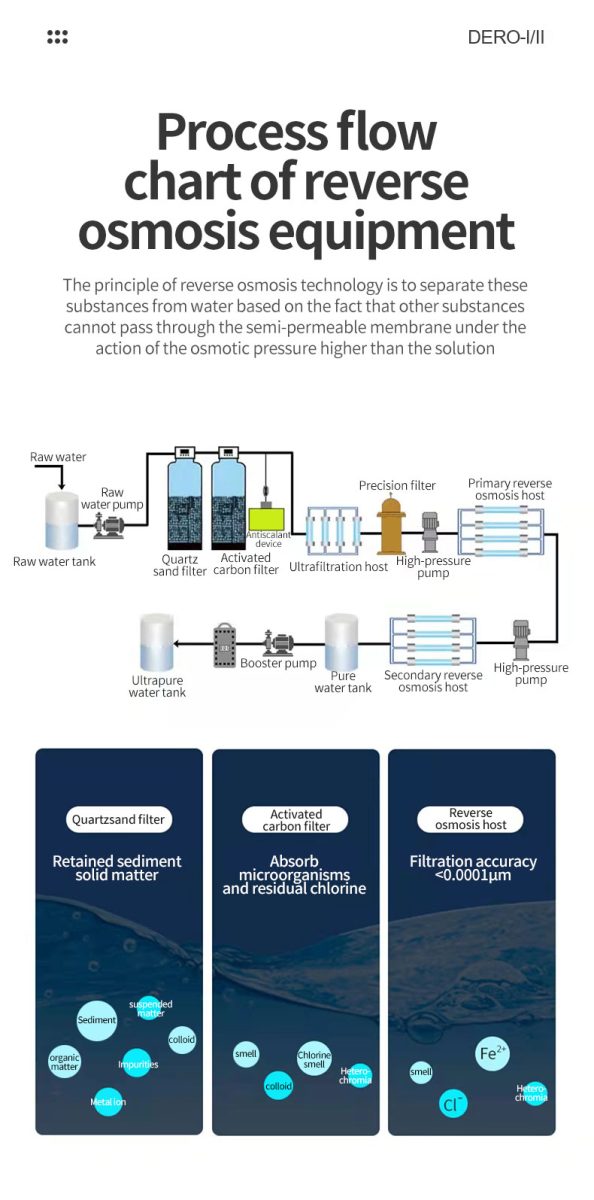
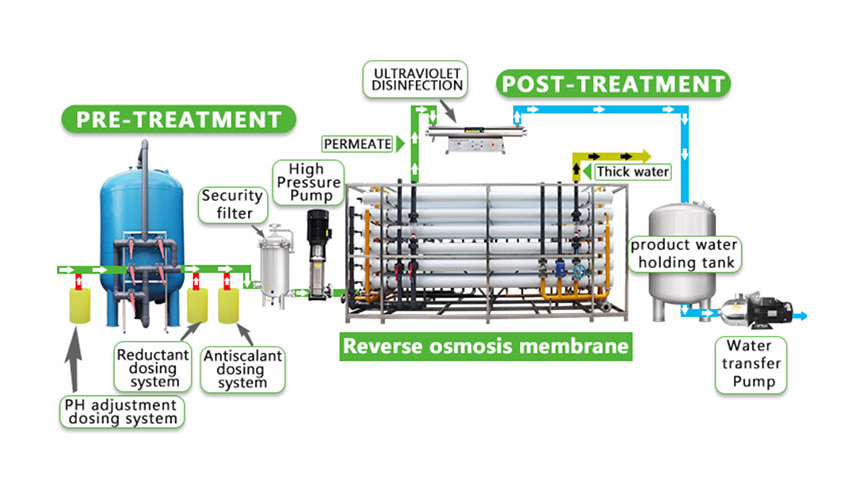
Reverse osmosis equipment
1. Equipment Introduction
Reverse osmosis water treatment equipment typically consists of three components: a raw water pretreatment system, a reverse osmosis purification system, and an ultrapurification post-treatment system. The primary purpose of pretreatment is to ensure that the raw water meets the inlet requirements of the reverse osmosis membrane separation components and ensures stable operation of the reverse osmosis purification system. Reverse osmosis membrane systems are the most cost-effective purification method for removing over 98% of ions and organic matter and 100% of microorganisms (theoretically) from raw water in a single step. Reverse osmosis is the most sophisticated membrane-based liquid separation technology. Operating pressure is applied to the inlet water (concentrated solution) side to overcome the natural osmotic pressure. When an operating pressure higher than the natural osmotic pressure is applied to the concentrated solution side, the natural osmotic flow direction of water molecules will be reversed, and some of the water molecules in the inlet water (concentrated solution) pass through the reverse osmosis membrane to become purified water on the dilute solution side. Reverse osmosis equipment can block all soluble salts and organic matter with a molecular weight greater than 100, but allow water molecules to pass through. The desalination rate of reverse osmosis composite membranes is generally greater than 98%. They are widely used in the preparation of industrial pure water and electronic ultrapure water, the production of drinking pure water, boiler water supply and other processes. The use of reverse osmosis equipment before ion exchange can significantly reduce the discharge of operating water and wastewater.
Reverse osmosis (RO) technology uses pressure to separate water and ions, thereby achieving purification and concentration. This process involves no phase change, generally requires no heating, and consumes very little energy. It offers numerous advantages, including low operating costs, no pollution, easy and reliable operation, and high-quality water. This makes it the most energy-efficient technology for desalination of seawater and brackish water. It has been widely used in numerous industries, including pharmaceuticals, electronics, chemicals, food, and seawater desalination. Reverse osmosis (RO) has become the preferred water treatment technology in modern industry and a key component of membrane separation technology.
(1) Fresh water can be extracted from seawater or brackish water;
(2) Organic matter, bacteria, colloids and other impurities dissolved in water can be easily removed to obtain high-purity water;
(3) Since the reverse osmosis process is a physical process, there is no phase change, which saves energy;
(4) The operation is simple and easy to automate, saving labor;
(5) The structure is compact and occupies a small area, thus reducing costs;
(6) As a concentration method, it can recover valuable components dissolved in the solution.
(1)Power industry: boiler feed water, cooling dams;
(2) Electronics industry: ultrapure water for semiconductor industry, integrated circuit cleaning water, formulation water;
(3) Food industry: formulation water, production water;
(4) Pharmaceutical industry: process water, preparation water, washing water, injection water, sterile water preparation;
(5) Beverage industry: formulation water, production water, washing water;
(6) Chemical industry: production water, wastewater treatment;
(7) Drinking water engineering: ultrapure water preparation, drinking water purification;
(8) Petrochemical industry: oil field injection water, petrochemical wastewater deep treatment;
(9) Seawater desalination: production and living water for island areas, coastal water-scarce areas, ships, seawater oil fields, etc.;
(10) Environmental protection field: recovery of precious metals and water in electroplating rinse water to achieve zero or micro discharge.