Fully automatic water softening equipment
1. Equipment introduction
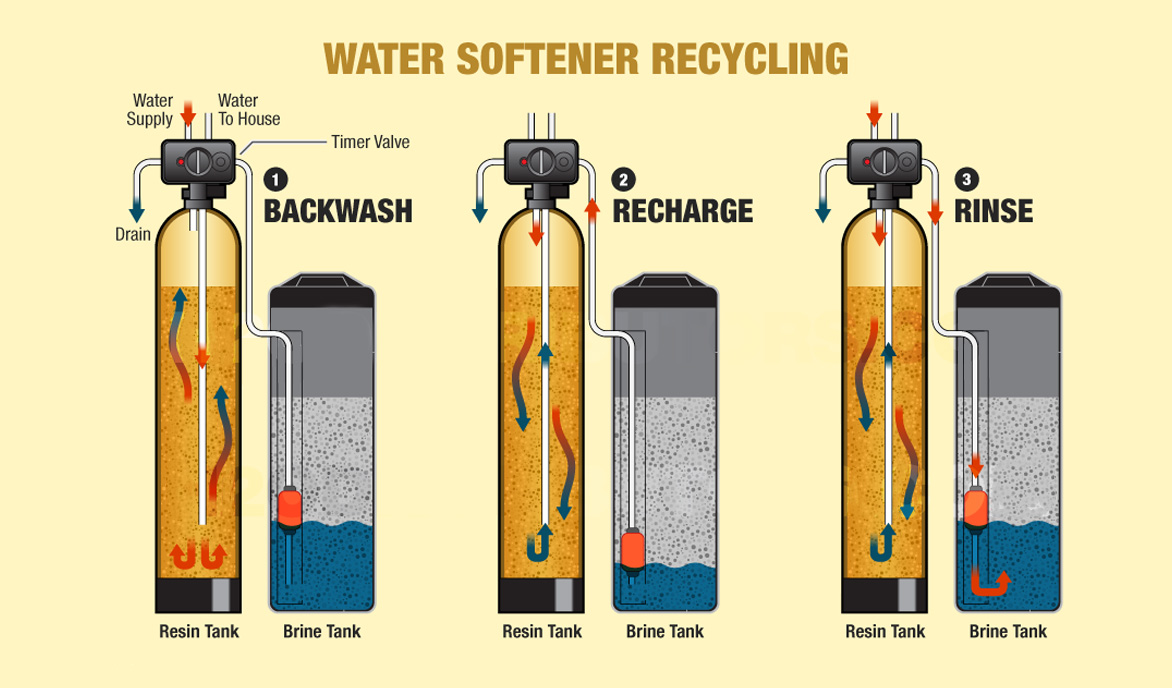
2. Working principle
Water softening equipment primarily utilizes anionic and cation softening. When the incoming water is from a deep well or has a very high hardness, water softening equipment is used to remove calcium and magnesium ions from the water, reducing the amount of calcium and magnesium ions in the water. If the water softener or softener fails, the concentration of calcium and magnesium salts on the reverse osmosis membrane increases dramatically, forming insoluble precipitates. This can clog the membrane pores, shorten the membrane's lifespan, and increase equipment maintenance costs.