Integrated sewage equipment
The main methods for treating printing and dyeing wastewater include physical, chemical, and electrolytic methods. A combination of chemical and physical methods often achieves better results. Adsorption is the most commonly used physical method, while chemical methods primarily include coagulation and oxidation.
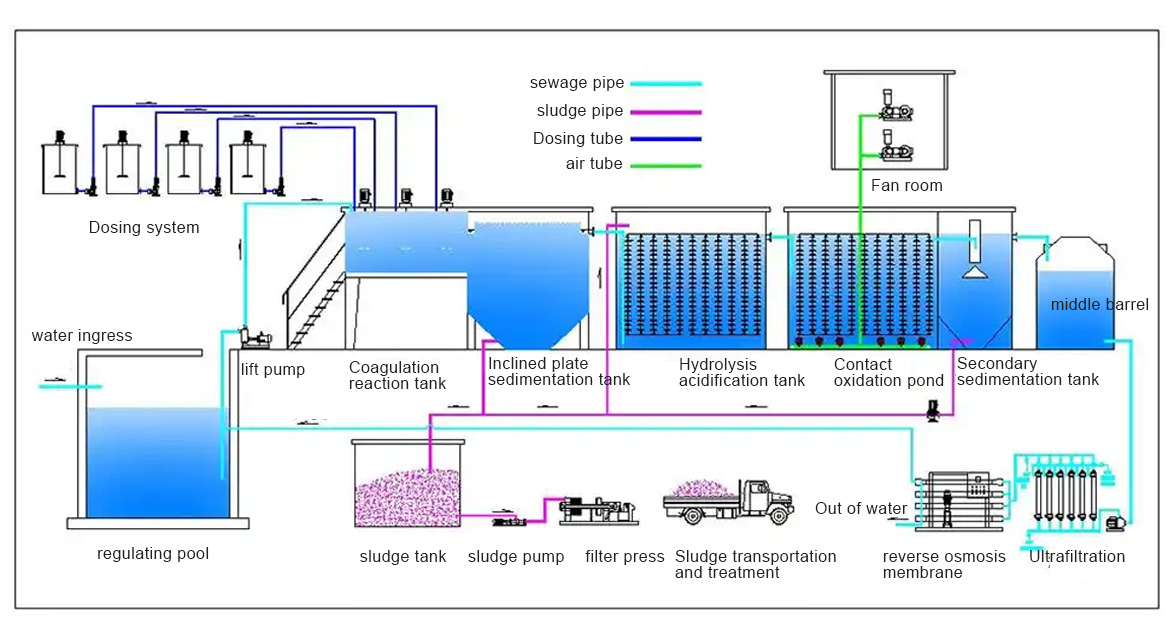
Physical treatment
Chemical treatment
Coagulation methods primarily include coagulation-sedimentation and coagulation-flotation. The coagulants used are mostly aluminum or iron salts, with basic aluminum chloride (PAC) exhibiting superior bridging adsorption properties, while ferrous sulfate offers the lowest price. The main advantages of coagulation methods include a simple process flow, easy operation and management, low equipment investment, minimal floor space, and high efficiency in decolorizing hydrophobic dyes. Disadvantages include high operating costs, high sludge production and difficulty dewatering, and poor treatment efficiency for hydrophilic dyes.
Electrolytic treatment
Statistically, due to differences in electrochemical properties, the COD removal rates of various dyes during electrolysis vary significantly. The order of COD removal rates is generally as follows: sulfur dyes, vat dyes - acid dyes, reactive dyes - neutral dyes, and direct dyes - cationic dyes.
