Laboratory EDI ultrapure water
High Purity | Stable Quality | Intelligent Control
The Laboratory EDI Ultrapure Water System is designed to produce high-resistivity ultrapure water for laboratories, research institutes, medical facilities, and pharmaceutical applications. By combining reverse osmosis (RO) and Electrodeionization (EDI) technology, the system continuously removes dissolved ions without chemical regeneration, ensuring stable and consistent ultrapure water quality.

Process Flow
Raw Water → Pretreatment → RO System → EDI Module → UV Sterilization → Ultrapure Water Storage → Point of Use

How EDI works
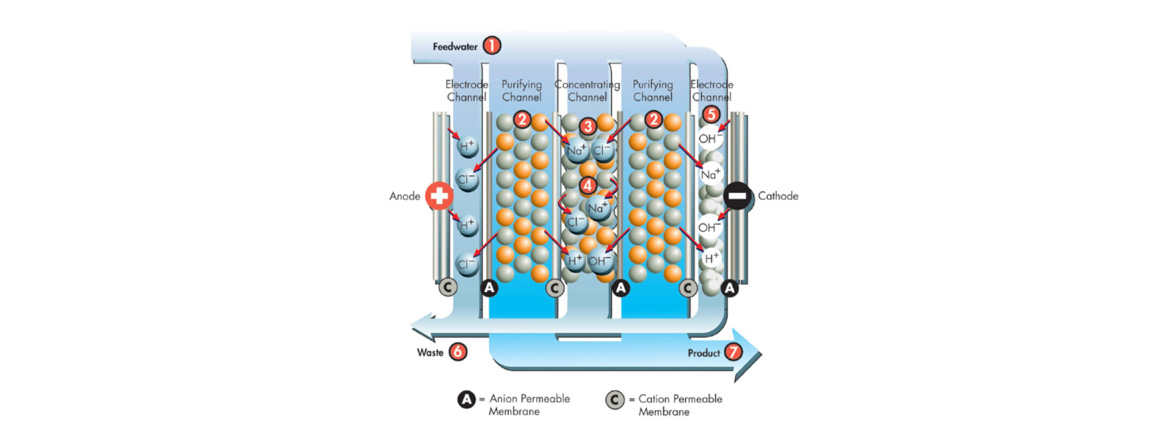
Key Advantages
-
Continuous ultrapure water production without chemical regeneration
-
High resistivity, stable output quality
-
Environmentally friendly and low operating cost
-
Compact, integrated design
-
Automatic PLC control and real-time monitoring
Technical Specifications (Reference)
-
Water resistivity: ≥15–18.2 MΩ·cm
-
Conductivity: ≤0.1 μS/cm
-
TOC: ≤5 ppb (optional polishing)
-
Capacity: 10–1,000 L/H (customizable)
-
Control mode: Fully automatic PLC system
Feed Water Requirement
-
RO permeate water
-
Low hardness and low SDI feed water
Application Areas
-
Analytical and research laboratories
-
Pharmaceutical and medical laboratories
-
Electronics and semiconductor labs
-
Chemical and biological research
-
University and institutional laboratories

Why Choose Us
-
10+ years ultrapure water system manufacturing experience
-
RO + EDI integrated solution provider
-
OEM & ODM service available
-
Stable performance and easy maintenance
-
Technical support and system customization

