Ozone Generator
Powerful Oxidation & Advanced Disinfection Solution
Product Overview
Ozone Generator is a high-efficiency system that produces ozone (O₃) for water disinfection, oxidation, deodorization, and color removal.
Ozone is a strong oxidizing agent, capable of rapidly killing bacteria, viruses, and microorganisms, while also breaking down organic pollutants without leaving harmful residues.
Ozone generators are widely used in drinking water treatment, wastewater treatment, industrial process water, food processing, aquaculture, and advanced oxidation systems.
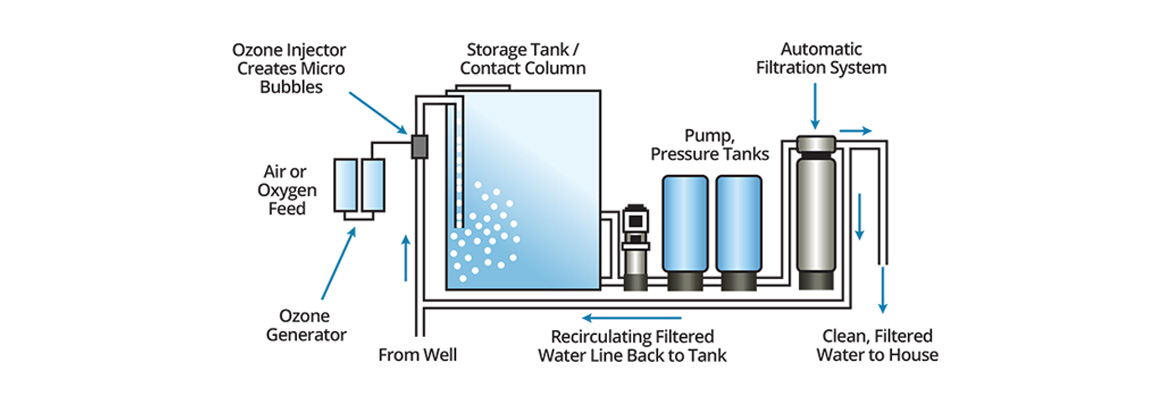
Working Principle
-
Oxygen or dry air is supplied to the ozone generator
-
High-voltage discharge converts oxygen into ozone
-
Ozone gas is injected into water through a diffuser or injector
-
Ozone oxidizes microorganisms and organic contaminants
-
Excess ozone decomposes naturally into oxygen

Key Features & Advantages
-
Strong oxidation ability
-
High sterilization efficiency
-
Effective deodorization & decolorization
-
No chemical storage required
-
No harmful residuals
-
On-site ozone generation
-
Automatic control & stable operation

Application Fields
-
Drinking water disinfection
-
Wastewater advanced treatment
-
Industrial circulating water
-
Aquaculture & fish farming
-
Food & beverage processing
-
Odor control & color removal
Optional Configurations
-
Oxygen concentrator
-
Ozone injector & diffuser
-
Ozone destruction unit
-
PLC control cabinet
-
ORP monitoring system
Advanced Oxidation Equipment
Ozone generators provide efficient, clean, and environmentally friendly disinfection and oxidation, making them an ideal solution for modern water treatment systems requiring high performance and low chemical usage.

